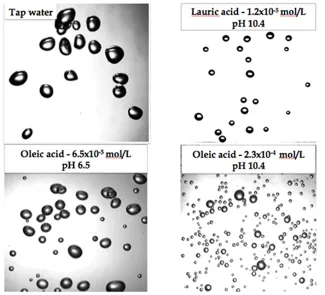
Separation of minerals can be achieved by a wide of range of methods, many of which rely on bulk particle properties such as size (e.g., screening) or density (e.g., dense medium separation). However, as the size of the treated particles decreases below 1 mm, and often below 0.1 mm, the importance of wet (water-based) methods increases and the surface properties of the particles start playing a dominant role in the selection of the separation method. Wettability of mineral surfaces by water (and by water-insoluble oils in some cases) and surface charge characteristics of particles are two broad groups of surface properties. Froth flotation is by far the most important technology for fine particle processing, and the process entirely relies on the surface properties of mineral particles.


Wettability and surface charge properties of mineral particles can be manipulated by addition of dedicated chemicals that act by adsorbing at the various interfaces (water-solid, water-gas, and gas-solid) and effecting different flotation responses from different minerals, thus allowing mineral separation to be achieved. Research in fine particle processing therefore involves various aspects of physical chemistry, electrochemistry, organic chemistry, and mineralogy, just to mention the main disciplines.
Understanding the surface properties of fine particles is also critical to tailings disposal, and water treatment, recovery, and recycling. Phenomena such as flocculation, coagulation, aggregation, and dispersion are primarily responsible for successful solid-liquid separation at fine particle sizes. Various types of flocculants, coagulants, and dispersants are widely applied in treatment of fine mineral tailings. Consequently, the interfacial behavior of polymers, surfactants, and simple ions is often the main subject of research in this area. Aggregation and dispersion phenomena in concentrated mineral suspensions also strongly affect the rheological properties of such suspensions.
Research and teaching in this field are often carried out using classical methods, such as contact angle, zeta potential, and Hallimond tube flotation measurements. However, complex techniques are also frequently employed in advanced research, e.g., infrared microscopy, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, x-ray computed tomography, or scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDX).
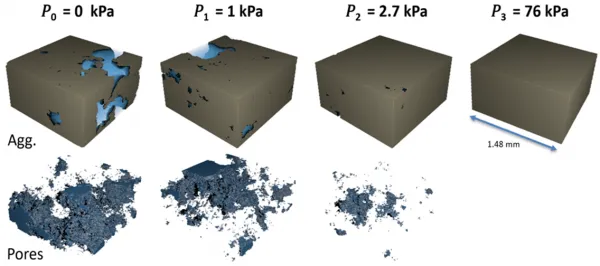
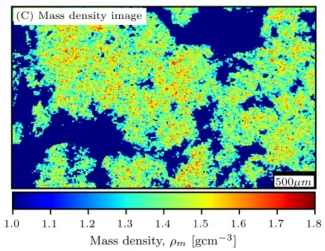
X-ray computed tomography of flocculated mineral sediments. Top left: raw grey-scale CT image of a sediment cross-section, top-right: the same image with densities assigned to aggregates after calibration, Bottom: 3D internal structure of interaggregate pores due to filtration at different pressures after “removing” the solid phase.